
Transmission media is the physical medium through which data is transmitted from one device to another in a network. Such a medium can either be wired or wireless. In both cases, one type has advantages over the other. The medium to be used depends on the distance, speed, interference, and cost. For example, wired media has great speed and reliability, while wireless media is convenient and flexible, especially over extended distances or when cabling is not feasible. To choose an appropriate medium for efficient, accurate, and reliable data communication, it is very important to know the types of transmission media. So let’s discuss them one by one!
Transmission Media in Computer Networks – What Is It?
Transmission media is the physical medium whereby data are transmitted between the devices on a network. These may be guided or unguided media in guidance, while distances, speeds, interference, and cost define the transmission medium in computer networks.
Also Read: Types of Firewalls in Computer Networks
Types of Transmission Media
Transmission media in computer networks can be broadly classified into two categories: Guided Media and Unguided Media.
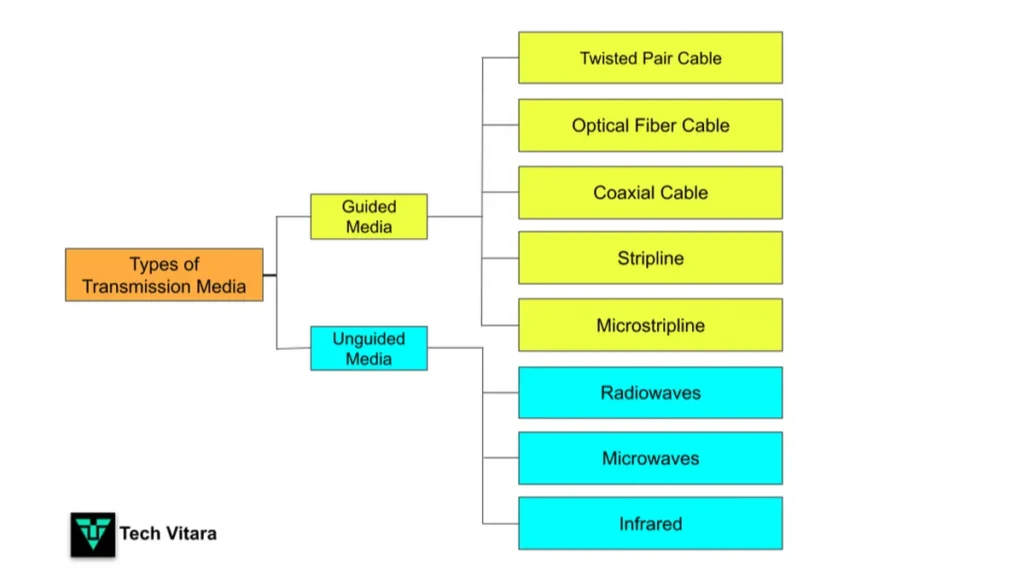
1. Guided Media in Computer Networks
Guided media, also known as wired transmission media or bounded transmission media, uses physical cables to guide signals from the transmitter to the receiver. The fact that cables are used means that the signals are restricted to a particular path. The following are the primary types of transmission media employed in guided media:
a. Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables consist of a copper core at the center, an insulator around it, a metal shield against noise, and a covering plastic layer. Guided media used in computer networks, coaxial cables are widely applied to cable TV, broadband access, and other data transmission.
Advantages:
- Improved protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- Can carry data over large distances
Disadvantages:
- Costly
- Hard to install
b. Twisted Pair Cable
This cable is made up of pairs of wires twisted in order to reduce interference. Twisted pair cables are in two types: shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP).
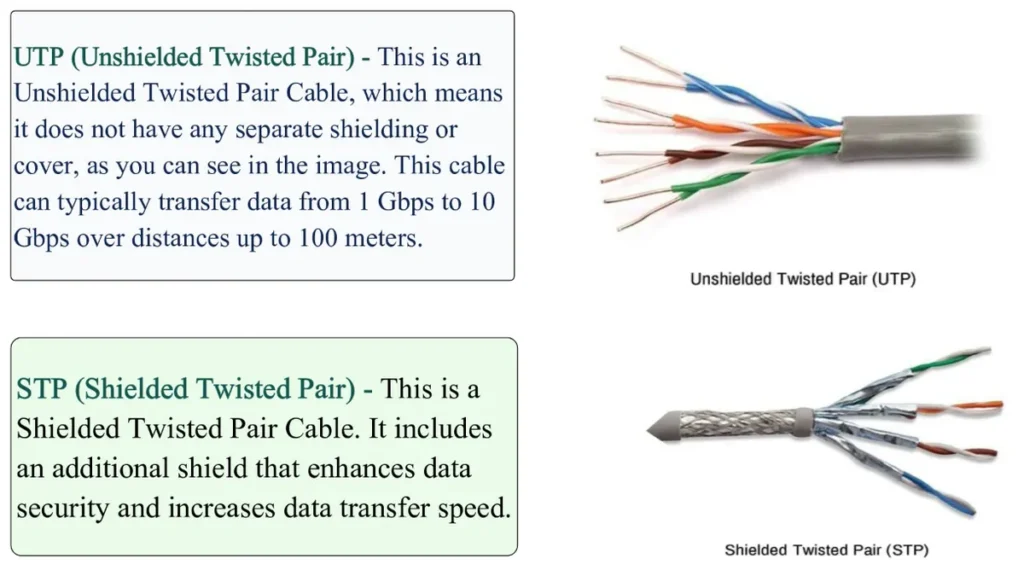
Advantages of STP:
- Eliminates external interference (EMI/RFI)
- Ideal for higher speeds than UTP
Disadvantages of STP:
- More costly
- Bulkier and more difficult to install
Advantages of UTP:
- Cheap
- Easy to install
Disadvantages of UTP:
- More susceptible to interference
- Limited capacity and distance
c. Fiber Optic Cable
Fiber optics use glass or plastic fibers to convey data in the form of light signals. Fiber optic cables are high-speed data transmission cables and are utilized for long-distance communication in networks.
Advantages:
- Very high-speed data transmission
- Insensitive to EMI
- Possible over long distances without loss of signal
Disadvantages:
- High installation and maintenance costs
- Fragile and requires special handling
2. Unguided Media in Computer Networks
Unguided media of computer networks means wireless transmission media that does not need cables. This medium transports data through electromagnetic waves in the air, which provides flexibility and mobility. Following are the prominent types of unguided media in computer networks:
a. Radio Waves
Radio waves are employed in long-distance communication, e.g., mobile phones and wireless networks. They are either omnidirectional (propagate in all directions) or directional (in a single direction).
Advantages:
- Easy to transport and install
- Ideal for long-distance communication
Disadvantages:
- Subject to interference due to physical objects and weather conditions
- Low bandwidth
Also Read: 5G networks vs. Wi-Fi 6 networks
b. Microwave Transmission
Microwave transmission involves the transmission of data through high-frequency electromagnetic waves. A line-of-sight between the sending and receiving antennas is needed.
Advantages:
- Fast data transfer
- Inexpensive and dependable
Disadvantages:
- Needs clear line-of-sight
- Prone to interference due to physical barriers and weather factors
c. Infrared Transmission
Infrared waves are used in short-distance communication. Remote control devices, wireless keyboards, and infrared computer-to-computer communication utilize this medium.
Advantages:
- Secure and high-speed data transfer
- Low power consumption
Disadvantages:
- Needs line-of-sight
- Short range and high attenuation
Differences Between Guided and Unguided Transmission Media
| Factor | Unguided Media | Guided Media |
| Transmission Medium | Wireless Signals (Radio Waves, Microwaves, Infrared) | Physical Cables (Coaxial, Twisted Pair, Fiber Optic) |
| Cost | Higher due to special equipment and infrastructure | Lower for short distances, increases with cable quality |
| Distance | Long distances, especially with satellite communication | Short to moderate distances, depending on the medium |
| Speed | Varies widely, can be high with some technologies (e.g., microwaves) | High speeds, especially with fiber optics |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, as it can be used in various environments without physical connections | Less flexible due to the physical setup |
| Interference | Prone to higher interference, especially in congested areas | Minimal interference, especially with fiber optics |
| Installation | Quick and easier installation, no need for physical cabling | Requires significant installation efforts, such as laying cables |
| Security | Can be more vulnerable to hacking or unauthorized access due to the open nature of wireless signals | Generally more secure due to physical cables, less prone to unauthorized access |
Conclusion
Transmission media in computer networks is a crucial part of ensuring smooth data transfer between devices. Depending on your requirements, you can choose from guided and unguided media in computer networks. Physical cables transmit the data in guided media (i.e., coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optics) and provide higher reliability and security. In contrast, unguided media (radio waves, microwaves, and infrared) offers flexibility and mobility with the use of wireless communication. Selecting a proper transmission medium in computer networks is crucial to maximize speed, range, and performance while reducing interference.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q. What is transmission media?
Transmission media refers to the physical medium via which data travels from one device to another within a network.
Q. What are the types of transmission media?
Guided (wired) and unguided (wireless) transmission media are the two primary types.
Q. What is guided transmission media?
Physical cables are used by guided transmission media to carry data.
Q. What is unguided transmission media?
Unguided transmission media carries data wirelessly via electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves, microwaves, and infrared.
Q. Why is the selection of transmission media significant?
The selection relies on considerations such as data speed, distance, cost, and susceptibility to interference, to guarantee maximum network performance.






Bombing Fishing? Sounds like my kinda party! Just stumbled upon it at Bombingfish.online and it’s looking pretty sweet. Check out the link bombing fishing.
Yo, heard pgslotpeh888 got some sweet slot action. Gonna throw a few spins their way and hope for a big payout! Wish me luck, fam!
Yo, just used dangnhap188bet to get in! Super easy, no hassle. Finally back to the game. Check it out here: dangnhap188bet
Just jumped on Jili8 and I’m digging the vibe for sure. They’ve got a solid selection of games and the site runs smoothly. Worth checking out if you’re looking for something new to play, that is jili8.
Heard Bahigoschweiz is the hot spot. Decided to see it myself. Game selection is awesome. Nice platform. Check it out. bahigoschweiz.
Alright folks, had my first run at Af88game. Had very nice gaming experience, all good looking games and website’s look and performance is good. af88game.